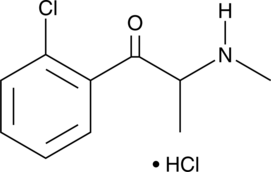
2-CMC (2-Chloromethcathinone) is a synthetic stimulant belonging to the cathinone class, structurally related to compounds like mephedrone and methcathinone. Cathinones are a class of substances chemically similar to amphetamines, but they contain a ketone group, which distinguishes them.
2-CMC is primarily studied for its stimulant and psychoactive properties, often in the context of pharmacological research.
Key Characteristics of 2-CMC:
- Chemical Structure: 2CMC contains a chlorinated phenyl ring attached to a cathinone backbone. The chlorine substitution at the second position gives it unique properties compared to other cathinones.
- Mechanism of Action: Like other cathinones, it is believed to act as a releasing agent and reuptake inhibitor of dopamine and norepinephrine, potentially leading to stimulating and euphoric effects.
- Effects: Research suggests it may produce increased energy, alertness, and enhanced focus, though data on its effects remain limited.
Research Applications:
2-CMC is used in scientific and laboratory research to:
- Investigate Neuropharmacology: Study its interactions with monoamine systems, particularly dopamine and norepinephrine.
- Explore Structure-Activity Relationships (SAR): Understand how the chlorination at the second position affects its potency and pharmacokinetics.
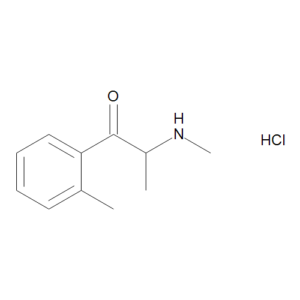
- Compare to Other Cathinones: Evaluate its effects in relation to substances like 4-CMC, methcathinone, and mephedrone.
Safety and Regulation:
- Potential Risks: Excessive doses or improper handling may cause adverse effects such as cardiovascular strain, anxiety, or insomnia.
- Legal Status: 2-CMC is classified as a research chemical in many jurisdictions, meaning it is not approved for human or veterinary use and is restricted to laboratory settings.
Important Information:
2-CMC is not approved for human or animal consumption. It is intended exclusively for scientific research and should only be handled by trained professionals under controlled conditions.

Yann –
Top grade