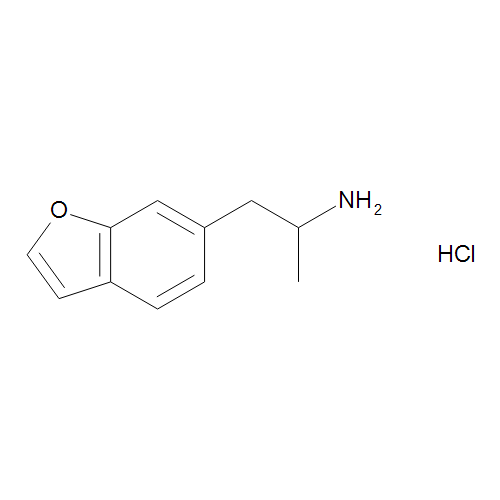
6-APB (6-(2-Aminopropyl)benzofuran) is a synthetic chemical compound that belongs to the benzofuran class, closely related to MDMA (3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine) and 5-APB. It is known for its stimulant and empathogenic properties, acting primarily on the serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine systems in the brain.
6APB is commonly studied for its effects on mood, empathy, and sensory enhancement, similar to other compounds in the same class.
Key Characteristics of 6-APB:
- Chemical Structure: 6-APB features a benzofuran ring attached to an amphetamine backbone, giving it psychoactive properties. The “6” refers to the position of the functional group on the benzofuran ring.
- Mechanism of Action: It acts as a releasing agent and reuptake inhibitor for serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine, promoting increased activity of these neurotransmitters.
- Effects: Research indicates that 6-APB produces euphoria, enhanced empathy, increased sociability, and heightened sensory perception.
Research Applications:
6-APB is primarily used in scientific research for:
- Neuropharmacology: Studying its interaction with neurotransmitter systems, particularly serotonin.
- Structure-Activity Relationships (SAR): Exploring how structural variations influence its effects and potency.
- Comparison Studies: Evaluating its effects in relation to similar compounds such as MDMA, 5-APB, and other benzofuran derivatives.
Safety and Regulation:
- Potential Risks: Excessive use may result in side effects like anxiety, insomnia, increased heart rate, and serotonin syndrome.
- Legal Status: 6-APB is regulated or prohibited in many countries and is considered a research chemical intended solely for laboratory studies.
Important Information:
6-APB is not approved for human or veterinary use. It is intended strictly for research purposes and should only be handled by qualified professionals in controlled environments.

Reviews
There are no reviews yet.