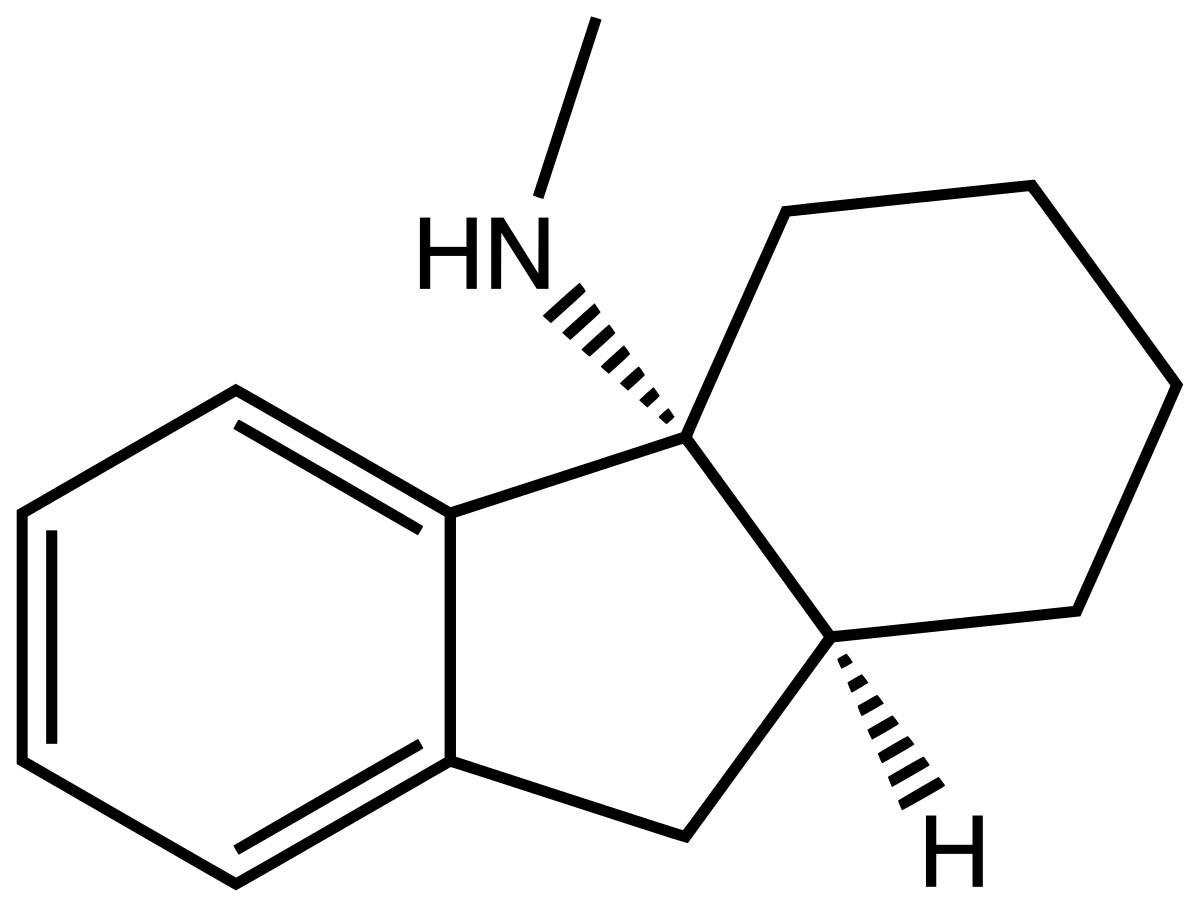
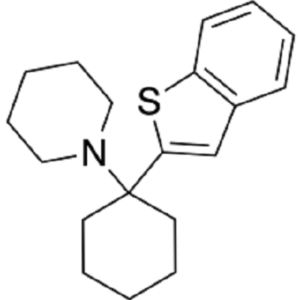
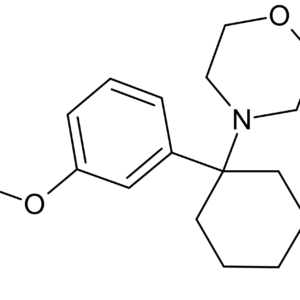
PD-137889 is a chemical compound classified as an arylcyclohexylamine derivative. This compound is a structural analogue of phencyclidine (PCP), sharing a similar chemical backbone but featuring modifications that distinguish it within the same family. PD-137889 is known to act as a dissociative anesthetic and an NMDA receptor antagonist, making it of interest in pharmacological and neurochemical research.
Key Characteristics of PD-137889:
- NMDA Receptor Antagonism: PD-137889 blocks NMDA receptors in the central nervous system, which are involved in synaptic plasticity, learning, and memory.
- Chemical Structure: It is similar to PCP but with structural differences that may alter its potency, binding affinity, and pharmacological profile.
- Research Significance: PD-137889 is primarily studied for its effects on neural pathways, dissociative mechanisms, and potential therapeutic applications.
Research Applications:
PD-137889 is utilized in:
- Neuropharmacology: Studying the role of NMDA receptors in neural activity and dissociative states.
- Receptor Binding Studies: Exploring how structural analogues of PCP interact with various receptor sites.
- Toxicological Research: Understanding the safety profiles and potential side effects of dissociative anesthetics.
Important Information:
PD-137889 is intended for research purposes only and is not approved for human or veterinary use. It should be handled by qualified professionals in controlled laboratory environments.

Aiden (verified owner) –
The product is firmly packed and discretely shipped.
Dominic (verified owner) –
Very fast delivery.
Angel (verified owner) –
The product is firmly packed and discretely shipped.
Kai (verified owner) –
Discrete service.