BTCP (Benocyclidine) is a synthetic compound classified as an arylcyclohexylamine, which is the same chemical family as phencyclidine (PCP) and ketamine. It was initially developed in the 1970s as part of research into potential treatments for neurological conditions like Parkinson’s disease, but it was never marketed for medical use.
Key Characteristics of BTCP:
- Chemical Structure:
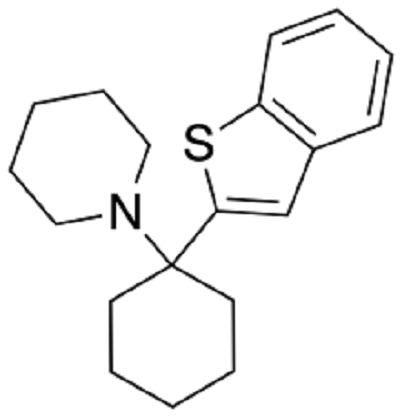
- The full name is 1-[1-(2-benzo[b]thiophenyl)cyclohexyl]piperidine.
- BTCP has structural similarities to PCP, with a benzo[b]thiophene group attached to the cyclohexane ring, which may influence its pharmacological effects.
- Its structure allows it to bind to various receptors in the brain.
- Mechanism of Action:
- BTCP is primarily known as a dopamine reuptake inhibitor (DRI). This means it blocks the reabsorption of dopamine into neurons, increasing dopamine levels in the brain.
- Unlike PCP or ketamine, BTCP is not an NMDA receptor antagonist, meaning it does not produce dissociative effects typical of other arylcyclohexylamines.
- Its mechanism suggests stimulant-like effects rather than dissociative anesthetic effects.
- Potential Effects:
- BTCP is reported to have stimulant properties due to its action on dopamine transporters. Effects may include:
- Increased energy and alertness.
- Enhanced mood or euphoria.
- Increased focus or cognitive stimulation.
- At higher doses, it may also produce anxiety or overstimulation, similar to other stimulants.
- BTCP is reported to have stimulant properties due to its action on dopamine transporters. Effects may include:
- Research and Medical Use:
- BTCP was studied as a potential treatment for conditions involving dopamine dysfunction, such as Parkinson’s disease, but development was discontinued due to insufficient therapeutic effects and concerns about side effects.
- It remains a research chemical with limited scientific and clinical data.
Risks and Concerns:
- Limited Research:
- BTCP is not well-studied, so its safety profile, long-term effects, and potential for harm are not fully understood.
- Potential for Abuse:
- As a dopamine reuptake inhibitor, BTCP may have a high potential for abuse and addiction due to its stimulant-like and euphoric effects.
- Adverse Effects:
- Likely side effects may include:
- Increased heart rate and blood pressure.
- Anxiety or paranoia at higher doses.
- Insomnia or restlessness.
- Addiction potential: Prolonged use may lead to dependency.
- Likely side effects may include:
- Overdose Risks:
- High doses could result in overstimulation, severe anxiety, or cardiovascular issues such as arrhythmias or hypertension.
Legal Status:
- The legal status of BTCP varies by country:
- It is typically unregulated but may fall under analog laws in jurisdictions that control substances related to PCP or dopamine reuptake inhibitors.
- Its distribution and use are generally restricted to laboratory or scientific research purposes.
Disclaimer:
BTCP is an experimental compound with limited data available on its safety and effects. It should only be handled in compliance with local laws and in controlled, scientific environments. Recreational use is strongly discouraged due to its potential for harm, including abuse, addiction, and unknown long-term effects. Always prioritize safety and harm reduction when studying or handling such substances.

Phoenix (verified owner) –
The product is firmly packed and discretely shipped.
Kai (verified owner) –
Very fast delivery.
Samuel (verified owner) –
Very fast delivery.
Paul –
The quality is good
Ryan (verified owner) –
Good quality Arylcyclohexylamine.