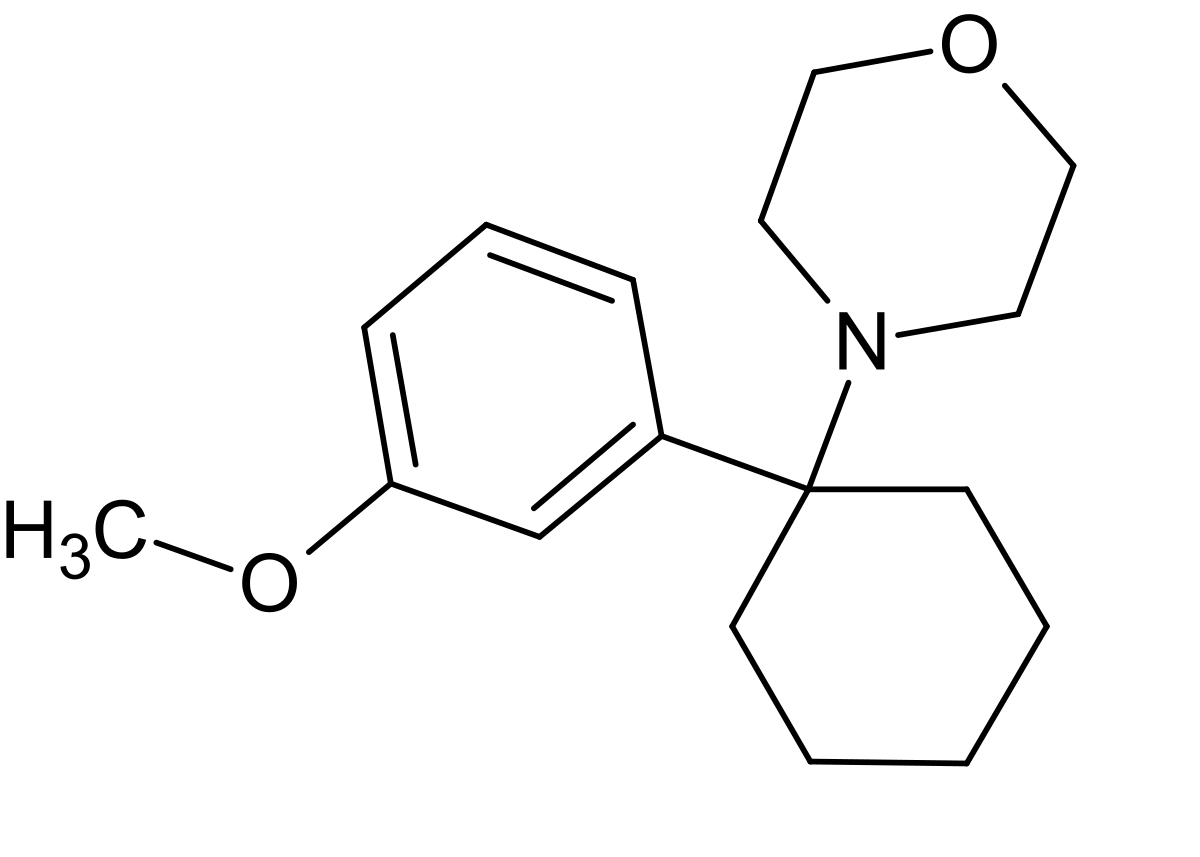
3-MeO-PCMo (3-Methoxyphencyclomorpholine) is a synthetic compound belonging to the arylcyclohexylamine class, known for producing dissociative anesthetic effects. It is structurally related to compounds such as 3-MeO-PCP, 3-MeO-PCE, and other dissociatives that act primarily as NMDA receptor antagonists.
Key Characteristics of 3-MeO-PCMo:
- Chemical Structure:
- 3-MeO-PCMo is a derivative of phencyclidine (PCP), modified by the addition of a methoxy (-OCH₃) group at the 3rd position of the phenyl ring and a morpholine ring in place of the piperidine ring found in PCP.
- These structural modifications may influence its pharmacological effects, receptor affinity, and overall potency.
- Mechanism of Action:
- Like other arylcyclohexylamines, 3-MeO-PCMo is thought to act primarily as an NMDA receptor antagonist, which blocks glutamate signaling in the brain. This mechanism is responsible for its dissociative effects, such as altered perception, detachment from reality, and anesthetic properties.
- It may also have activity at other receptor sites, including serotonin, dopamine, and sigma receptors, which could contribute to additional psychoactive effects.
- Psychoactive Effects:
- While detailed studies are limited, anecdotal reports from users suggest effects similar to other dissociative anesthetics, including:
- Dissociation and detachment from surroundings.
- Altered sensory perception (e.g., visual or auditory distortions).
- Euphoria or mood enhancement.
- Cognitive changes, such as introspection or thought loops.
- The specific effects, intensity, and duration of 3-MeO-PCMo are not well-documented, but it likely shares some characteristics with related compounds like 3-MeO-PCP and 3-MeO-PCE.
- While detailed studies are limited, anecdotal reports from users suggest effects similar to other dissociative anesthetics, including:
- Research Chemical:
- 3-MeO-PCMo is classified as a research chemical, meaning it is not approved for medical or therapeutic use. It is primarily used in laboratory research to study its pharmacology and effects.
Risks and Concerns:
- Limited Research:
- There is little to no clinical or peer-reviewed research on 3-MeO-PCMo. Its safety, pharmacokinetics (how the body processes it), and long-term effects remain largely unknown.
- Potential for Abuse:
- Like other dissociatives, 3-MeO-PCMo may have a potential for psychological dependence due to its euphoric and dissociative effects.
- Adverse Effects:
- Possible negative effects could include:
- Confusion and disorientation.
- Motor impairment or loss of coordination.
- Anxiety, paranoia, or psychosis, particularly at higher doses.
- Nausea, increased heart rate, or dizziness.
- Potential bladder toxicity, a concern with prolonged or heavy use of arylcyclohexylamines.
- Possible negative effects could include:
- Overdose Risks:
- High doses could lead to severe dissociation, psychosis, or loss of consciousness, making it potentially hazardous.
Legal Status:
- The legal status of 3-MeO-PCMo varies by country. In some jurisdictions, it may be regulated as a controlled substance or analog of PCP, while in others, it may remain unregulated.
Disclaimer:
3-MeO-PCMo is an experimental compound with significant risks. It should only be handled in compliance with local laws and regulations and under controlled, scientific conditions. Recreational use is strongly discouraged due to its potential for harm, including physical and psychological side effects.


Reviews
There are no reviews yet.